The global IT spending on cloud computing is to reach USD 1.3 trillion by the end of 2022.
Companies are rapidly shifting towards cloud computing, as statistics represent 60% of corporate data stored on the cloud. Where there are many segments of cloud computing, Function as a Service (FaaS) is emerging as its fastest-growing segment.
This blog is all about FaaS: What is FaaS, how it works, why use FaaS, its advantages, use cases, implementation, best practices, and top 5 service providers. However, before directly jumping on FaaS let us understand some important aspects of cloud computing.
Important Insights into Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the use of remote servers over the internet to store, process, and manage data.
Cloud computing has many segments such as PaaS is Platform as a service, SaaS is Software as a Service, IaaS is Infrastructure as a Service, FaaS is Function as a Service and CaaS is Container as a Service. How does it work? Let’s see.
How to choose a Cloud Service?
There is nothing like superior or inferior when it comes to choosing a cloud service for cloud computing. However, which cloud service to choose entirely depends on the requirements of your application. The below flowchart will make this more understandable.
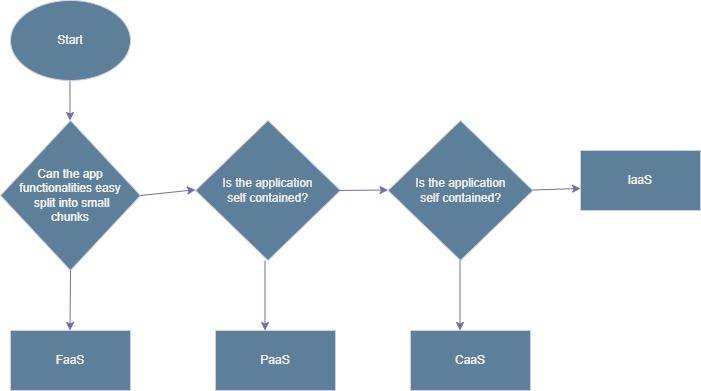
So, now that you are clear about when to use FaaS, let us jump to the point.
What is Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)?
FaaS is a cloud computing service that offers a platform to users for developing, deploying, or managing application functionalities without the hassle of building or maintaining the infrastructure. FaaS is often used for developing microservices applications.
If you are deploying software applications on the internet, you must provide, execute and manage the entire cloud infrastructure. Developing applications on Faas will leave the entire process of deployment to the service provider, enabling you to focus on the individual functions of your application code.
How does FaaS work?
FaaS (Function as a Service) is a kind of cloud computing service enabling developers to build, compute, deploy, and run applications and services. The benefit of FaaS is that it can create and upload individual functions without having to maintain its infrastructure which leads to coding accuracy. These functions are specifically executed when there is a specific trigger such as a user request or an event like a new data record gets added to the database.
This process becomes autonomous when different functions work in a chain, i.e., completing one function triggers another function to execute.
When a function gets triggered, it demands the cloud provider to activate the server. On successful execution of the function, the server goes down.
What is FaaS Serverless Computing?
Serverless is a misnomer; FaaS and Serverless are not contradictory. In fact, FaaS falls under the category of serverless computing. Where serverless signifies a service category in which the server configuration, management, or billing stays invisible to the end user; FaaS focuses on an event-driven computing paradigm where the application code runs only in response to events/requests.
Applications following the FaaS model are based on serverless architecture, where the cloud providers take care of the servers on behalf of their users and distribute machine resources on demand.
The on-demand functionality in FaaS allows its supporting infrastructure to power down and stop incurring charges while not in use. This is the main reason users opt for FaaS.
What are the advantages of FaaS?
Improved code delivery:
FaaS can help you distribute the server into independent functions that can be automatically scaled. So, no need to worry about managing the infrastructure. Developers just have to focus on the application code, hence assuring higher productivity.
Flexibility:
With Faas, users can write and deploy functions in various languages and frameworks. Moreover, it also provides greater flexibility as compared to other serverless computing frameworks in terms of optimizing the development process.
Integration:
FaaS can be seamlessly integrated with other services and systems. It allows performing seamless integration with the existing architecture and still does not hamper the functionality of the entire cloud infrastructure.
Cost-effective:
Billing in a FaaS model is based on computation time. It has an autonomous logging system that keeps a track of the number of times functions are rendered and the time taken to render a function. So, you only have to pay for what you use, and when you use it.
Auto-scaling:
With FaaS you can quickly scale the functions up or down. These functions can be automatically, instantly, and independently scaled as per the demand.
Optimum resource utilization:
Resources are never idle. Once the function is executed, no code runs and no server sits idle, hence no cost is incurred. Resources are only invoked when a function is triggered.
High Availability:
With FaaS you can enjoy the robust cloud infrastructure across multiple availability zones of various geographic regions. You can deploy FaaS on multiple locations without any incremental cost.
Maintenance:
Your FaaS provider manages all the maintenance of operating systems, connections, container images, etc.
Security:
Your cloud provider safeguards the security of infrastructure as well as ensures that functions are being executed within a secure perimeter and that all updates are in place.
Use Cases of FaaS
Data Processing
FaaS is used for data processing (batch processing/stream processing), ETL (Extract-Transform-Load), IoT (Internet of Things), mobile applications, and web applications.
Event Driven Computing
Event-driven computing combined with FaaS inherently provides loose coupling enabling service abstraction and isolation, independent scale, and deployment flexibility. As functions are inherently fine-grained, they can operate individually just like individual musicians do.
Microservices
There are systems for serverless computing that compose independent, small and interconnected units of functionality. They are most favored over the larger bundles of functionality. Hence, a lot of existing best practices in designing microservices are applied in serverless computing as well. And that is why FaaS platform implementations inherently follow the microservices model.
Performance Enhancement
FaaS enables applications to run computations on a massive scale in less time. This enhances the app’s performance. In addition, it can handle high-volume and parallel workloads. Also, it allows transactions to isolate and scale easily. So, you can use FaaS for data processing, encoding, formatting conversion, and data aggregation, as well as to create backend systems.
Managing APIs
FaaS can help in integrating and implementing APIs for new as well as already existing applications without changing their functionalities.
On-demand functionality
It enables the power-down feature of any infrastructure, resulting in cost-cutting and reducing the billing amount.
Developer friendly
Developers find working with FaaS convenient as it simplifies application development and sending updates to users becomes easy. Moreover, the infrastructure is fully optimized, and developers only need to focus on writing the code. This results in fast development, fast update, and quick customer response.
Which are the top 5 FaaS service models with their key features?
1. AWS Lambda
Amazon Web Services Lambda is a FaaS platform where developers can render their code on the highly available compute infrastructure. Here, developers are only charged for the time taken to run the code.
Key Features:
· AWS Lambda maintains the server and OS on behalf of users.
· It monitors the server and OS for error-free performance.
· It has an auto-scaling feature and allows high flexibility.
· It automatically maintains the log of events and keeps a track of resources in use.
2. Google Cloud Functions
Google Cloud Functions are one of the top FaaS providers across the globe. It offers an ecosystem where developers can render their code without being concerned about server management or administration.
Key Features:
· No requirement to administer or manage the server
· Auto scalable
· Allow developers to use third-party services as building blocks rather than building the code from scratch.
3. Azure Cloud Functions
Microsoft Azure Cloud Functions offer developers a platform to build applications more efficiently with serverless cloud computing.
Key Features:
· No restriction to the tech stack. Developers can use any programming language or framework for building or deploying the functions.
· It has an amazing feature to monitor performance. You can easily identify weak areas by using this feature.
· By using the in-built DevOps and integrated tools, developers can improve debugging capabilities and speed up end-to-end development.
4. IBM Cloud Functions
If you are a service provider, then IBM Cloud Functions is a simple and reliable option to choose from. There is no need to manage the server, OS, or infrastructure, plus you can easily render the backend code of your app.
Key Features:
· Cost-effective
· Highly scalable
· To execute a code, you can trigger an event or use REST API.
5. Oracle Functions
Another good option for serverless computing.
Key Features:
· Easy integration
· Auto Scaling
· Supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
Best Practices to deploy FaaS Easily and More Effectively
One function One action
Design a function to render only one action in response to a request. Keep your code snippet small, lightweight, and efficient so that the functions can load and execute quickly.
Avoid functions calling other functions
FaaS works efficiently owing to its independent and incremental functions. Isolation of functions is important to maintain their value. Hence, do not make functions call over other functions because too many functions can increase the cost and reduce FaaS value.
Limit the use of libraries
Using many libraries at a time can lower the speed of functions and make them difficult to scale.
Monitor function performance
Regularly monitoring function performance and resource usage ensures that functions are running efficiently and within their allocated resource limits.
Use version control
You can use version control tools, such as Git, to manage and track changes to function code. This allows for easy rollbacks and debugging in case of issues.
Test functions thoroughly
You need to thoroughly test functions before deploying them to production, including testing for edge cases and error handling.
Use error logging and monitoring
Make sure you implement error logging and monitoring to detect and address issues in a timely manner.
Use a deployment pipeline
Use a deployment pipeline to automate the build, test, and deployment process for functions. This can reduce the time and effort required to deploy updates and new features.
Use a staging environment
Use a staging environment to test and validate new features and updates before deploying them to production.
Use appropriate resource allocation
Allocate appropriate resources to functions based on their expected workload and performance needs.
Wrapping up
The global FaaS market size was valued at USD 3.02 billion in 2018 and is expected to garner USD 23.01 billion by 2025, accelerating at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 29.7% from 2019 to 2026.
FaaS is one of the fastest-growing cloud service models as it has reduced the dependency on system software and the availability of physical infrastructure.
The below image depicts the increase in the adoption rate of FaaS in various industry verticals over the years.
With the emergence of microservices, the adoption rate of FaaS is dramatically increasing. With a developer-friendly architecture and burdenless development process, FaaS seems to create new avenues for growth in the near future.
Cubet can help you with cloud computing. We are known to deliver quality cloud-based services. Contact our best Cubet developers for a FREE consultation right away!
Have a project concept in mind? Let's collaborate and bring your vision to life!
Connect with us & let’s start the journey
Share this article

Get in touch
Kickstart your project
with a free discovery session
Describe your idea, we explore, advise, and provide a detailed plan.


























