Intelligence Integration for Scalable, Enterprise-Ready AI
Artificial intelligence has become a permanent fixture on enterprise technology roadmaps. Organizations across industries are experimenting with predictive analytics, automation, generative AI, and intelligent assistants. Yet despite growing investment, many initiatives struggle to move beyond isolated pilots or limited deployments.
The challenge is no longer access to AI tools or models. It is how intelligence is integrated into the enterprise into existing systems, workflows, data architectures, and governance frameworks. As AI adoption matures, enterprises are increasingly recognizing that sustainable value depends on architectural coherence rather than standalone innovation.
This has led to a shift toward intelligence integration as a core enterprise capability.
The Fragmentation Challenge in Enterprise AI
Most enterprises operate within complex digital ecosystems built over the years, often decades of investment. ERP platforms, CRMs, data warehouses, legacy applications, and modern SaaS products coexist, supporting critical business functions.
When AI is introduced without a clear integration strategy, several patterns commonly emerge:
AI tools operate outside core operational systems
Insights remain confined to dashboards rather than influencing workflows
Multiple vendors introduce fragmented decision logic
Data governance becomes difficult to enforce consistently
Scaling pilots into enterprise-wide capabilities proves challenging
In such environments, AI exists, but it does not meaningfully participate in how work is executed.
What Intelligence Integration Means
Intelligence integration refers to the practice of embedding AI capabilities directly into existing enterprise systems and workflows, rather than deploying them as separate platforms or tools.
This approach emphasizes:
Workflow continuity over tool proliferation
Architectural alignment over rapid experimentation
Governed data access over isolated intelligence
Long-term scalability over short-term optimization
When intelligence is integrated effectively, it becomes an extension of enterprise software, supporting decisions, automating processes, and improving outcomes without disrupting established operations.
Enterprise Approaches to AI Adoption
In practice, organizations typically follow one of three approaches when adopting AI. Each carries different implications for scalability, governance, and long-term strategic value.
AI Adoption Approaches — Enterprise Comparison
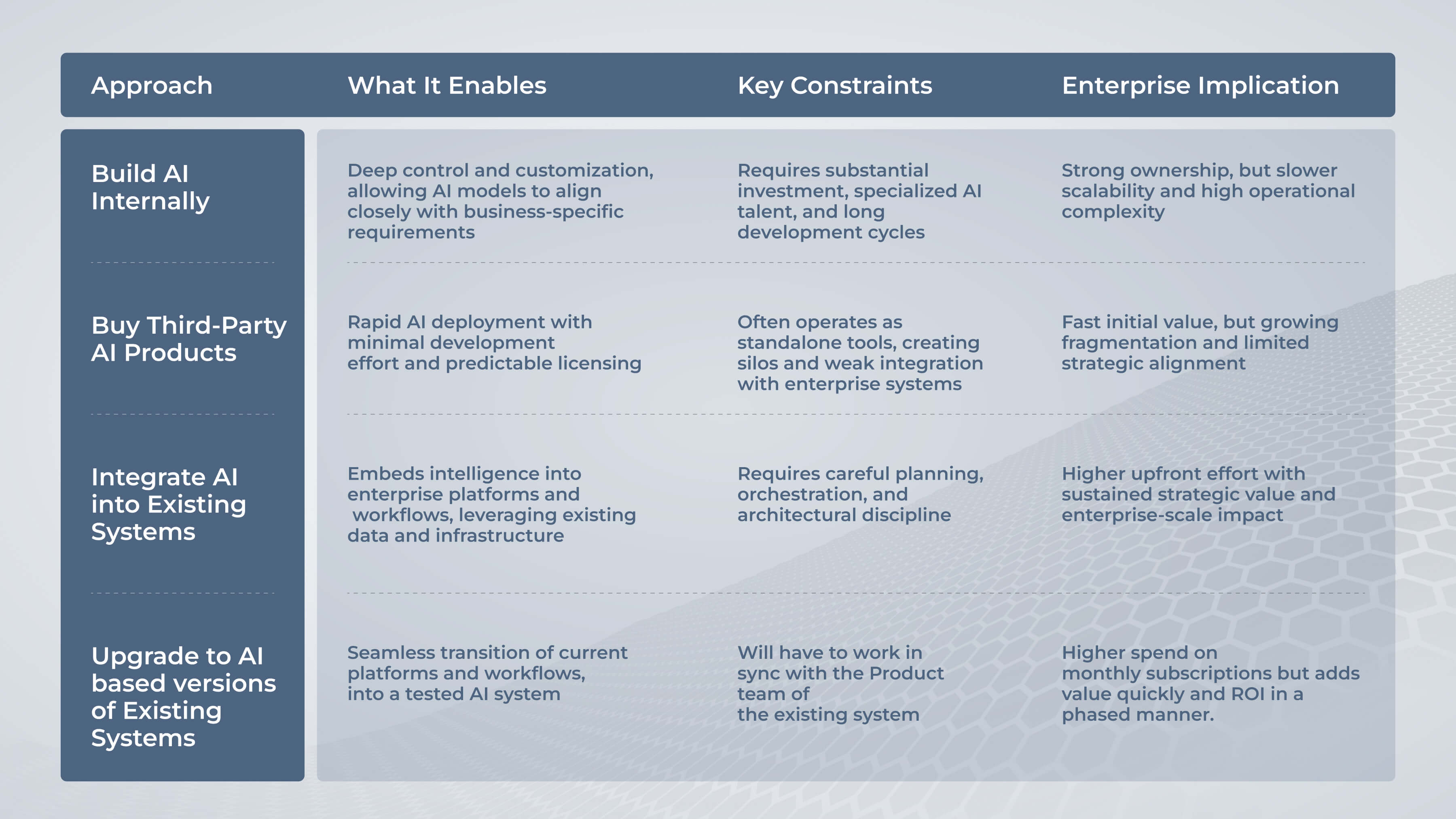
As enterprise environments grow more complex, intelligence integration is increasingly favored for its ability to balance innovation with stability.
From AI Experiments to Enterprise Capability
A defining characteristic of intelligence integration is its incremental nature. Rather than attempting wholesale transformation, intelligence is introduced at specific decision points where it can deliver measurable value.
Common examples include:
Predictive insights embedded into operational dashboards
AI-assisted validation within approval and compliance workflows
Intelligent document processing integrated into core systems
Decision support for planning, forecasting, and resource allocation
Embedded assistants within enterprise applications
In each case, AI augments existing systems rather than replacing them.
Architectural Considerations That Shape Success
Successful intelligence integration requires more than technical connectivity. It demands architectural discipline across several dimensions:
Data alignment: Ensuring AI operates on trusted, governed enterprise data
Workflow orchestration: Embedding intelligence where actions occur
Interoperability: Supporting both legacy and modern systems
Security and compliance: Maintaining enterprise-grade controls
Extensibility: Allowing intelligence capabilities to evolve without re-architecture
These considerations often determine whether AI initiatives mature into foundational enterprise capabilities or remain isolated from experiments.
Technologies and Platforms We Work With
Intelligence integration in the enterprise requires flexibility across models, platforms, and deployment environments. The focus is not on a single technology stack, but on selecting and integrating the right components based on enterprise context, governance requirements, and long-term scalability.
Languages
Python – Primary language for AI/ML model development, data pipelines, automation, backend services, and integrations
TypeScript (Node.js) – Used for service orchestration, APIs, real-time integrations, and event-driven workflows
Frameworks (Agents / RAG)
Custom Python-based agent frameworks – Tool calling, workflow orchestration, multi-step reasoning
RAG pipelines – Document ingestion, embedding generation, retrieval, ranking, and response grounding
OpenAI / Azure OpenAI APIs – Enterprise-grade LLM integration
Hugging Face Transformers – Open-source LLMs and embedding models
Frameworks (Training & ML Pipelines)
PyTorch – Primary framework for deep learning and custom model training
TensorFlow / Keras – Used where ecosystem compatibility or existing models require it
Hugging Face Trainer – Model training, fine-tuning, and evaluation
AWS SageMaker – Managed training jobs, pipelines, and scalable inference
Models
OpenAI GPT models – Text generation, summarization, reasoning, and copilots
Meta Llama models – Self-hosted or cloud-hosted open-weight LLMs
Open-source Hugging Face models – Domain-specific and task-optimized models
Models (Fine-tuning & Vision)
YOLO-based models – Object detection and real-time vision use cases
Custom CNN architectures – Classification, detection, and domain-specific vision tasks
PyTorch-based fine-tuning – Transfer learning and performance optimization
Vector Databases (Memory Layer)
pgvector – Postgres-based vector storage for RAG systems
FAISS – High-performance in-memory similarity search
Elasticsearch (vector search) – Hybrid keyword + vector retrieval
Platforms (Development & Deployment)
AWS – EC2, SageMaker, EKS for AI workloads and scalable deployment
Azure – Azure OpenAI and Azure AI Services for enterprise clients
Docker – Containerized model serving and application deployment
Low-Code & Automation
Custom automation frameworks – API-driven orchestration and workflows
n8n / similar tools – Lightweight integrations and process automation where appropriate
This breadth allows intelligence to be integrated across cloud, on-prem, and hybrid enterprise environments without constraining architectural choices.
Examples of Enterprise AI Implementations
Rather than isolated tools, intelligence integration typically manifests as embedded capabilities within existing enterprise systems. Common implementation patterns include:
Intelligent Document Processing
Automating the extraction, validation, and classification of documents such as invoices, contracts, medical records, or compliance filings, integrated directly into ERP or workflow systems.Decision Intelligence in Core Workflows
Embedding predictive and prescriptive insights into planning, approval, and forecasting workflows, enabling context-aware decision support rather than post-hoc analysis.AI-Assisted Operations and Support
Integrating AI assistants within internal tools to support operations teams, customer support agents, or analysts, enhancing productivity without replacing existing systems.Predictive Analytics for Business Planning
Using historical and real-time enterprise data to forecast demand, risk, or performance, with outputs embedded into dashboards and operational systems.Computer Vision and Inspection Systems
Applying vision models within quality control, safety monitoring, or asset inspection workflows, integrated with enterprise reporting and compliance systems.Enterprise Clinical Knowledge Assistant (RAG-based)
An AI assistant integrated with hospital EMR/EHR systems that allows clinicians to query patient records, clinical guidelines, SOPs, and medical literature using natural language.Automated Medical Imaging Triage & Review
An AI-powered computer vision system that analyses radiology images (X-ray, CT, MRI) to flag high-risk cases such as fractures, lung opacities, or abnormal growths.Intelligent Revenue Cycle & Coding Assistant
An enterprise AI solution that reviews clinical notes, discharge summaries, and procedure records to suggest ICD/CPT codes and detect billing anomalies.
Patient Engagement & Post-Care Follow-up Assistant
A conversational AI assistant that supports patients after discharge by answering care instructions, medication queries, and follow-up reminders.
Each of these implementations focuses on augmenting enterprise processes, not introducing parallel AI tools.
Strategic Outcomes of Integrated Intelligence
When intelligence integration is executed with architectural foresight, enterprises typically observe consistent outcomes.
Existing technology investments deliver greater returns as intelligence enhances core platforms rather than duplicating them. Decision-making improves as insights are unified across systems and departments, reducing fragmentation. Governance and compliance are strengthened by keeping intelligence within enterprise-controlled environments.
Incremental adoption accelerates time to value while reducing organizational and technical risk. Over time, intelligence evolves into a scalable capability, aligned with long-term digital roadmaps and adaptable to changing business priorities.
A Disciplined Framework for Enterprise AI
At Cubet, this perspective is applied through the AI³ Approach, which frames intelligence integration around three principles:
Intelligence: Identifying where AI meaningfully improves decisions and outcomes
Innovation: Rethinking workflows without introducing unnecessary complexity
Impact: Measuring success through tangible, business-aligned results
This framework emphasizes architecture, governance, and measurable outcomes, ensuring AI initiatives evolve into enterprise-grade capabilities rather than isolated deployments.
Closing Perspective
As AI adoption accelerates, the differentiator for enterprises will not be the number of models deployed, but the quality of integration achieved.
Organizations that embed intelligence into their systems, workflows, and decision structures are more likely to realize sustained value, transforming AI from an initiative into an enduring enterprise capability. In this context, intelligence integration is not simply a technical choice, but a strategic discipline, one that aligns innovation with enterprise reality.
Want to move beyond pilot projects and make AI a real part of your enterprise? Talk to us about building integrated, on-prem intelligence that fits your systems and scales with your business.
Have a project concept in mind? Let's collaborate and bring your vision to life!
Connect with us & let’s start the journey
Share this article

Get in touch
Kickstart your project
with a free discovery session
Describe your idea, we explore, advise, and provide a detailed plan.



























