Laravel-Model
Eloquent ORM is an Object Relational Mapper that enables us to define relationship with the model, such that once the relationship is defined we can perform database manipulation without explicit query.
Relationship type -:
- OnetoOne
- OnetoMany
- ManytoMany
- HasManyThrough
- Polymorphic one-to-one/one-to-many
Implementation
1.Install laravel
2.create new database in mysql(blog)
3.update db details in config/database.php
one-to-one relation
Example : schema
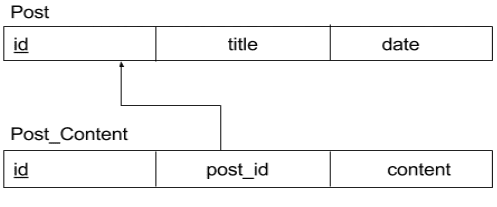
Here post_id is the foreign_key of Post_Content, So in order to create the relation, first we need to create the model
Now we can access the data using $blog->blog_content
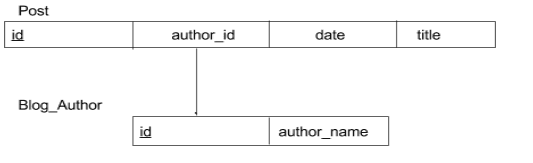
One-to-Many
For each blog there is only a single author and a single author can have many post(one-to-*).
And now let’s establish a one-to-* relation using hasMany functions.
$blog_author->post we get all the posts of a single author. Here we need to get the author details of a single post, for each post there is a single author, within the Post model including belongsTo relation.
In the post, we get the details of author using $post->author->author_name
In Author, we can loop through all the post of an author using $author->post
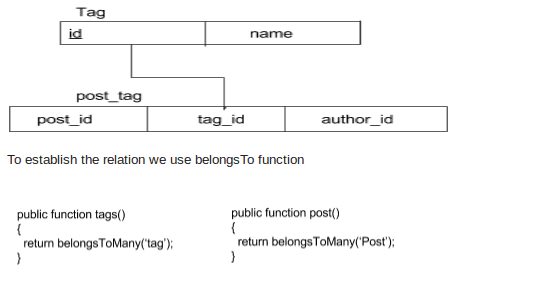
Many-To-Many
Each post have many tag and each tag can have many post.
Laravel Model Relationships
Here all the above methods used to read data, While creating a new post we need to insert data to the Post, Content, Author etc. we can perform this using query builder save()
$post = Post::create(array(‘title’ => Input::get(‘title’));// insert into table post
$text = Text::create(array(‘text’ => Input::get(‘text’)); // insert into table content
$post->text()->save($text);
Conclusion
This article includes the fundamentals of Eloquent ORM model. Eloquent ORM implementation is really fast and the interaction with the database is very simple.
Have a project concept in mind? Let's collaborate and bring your vision to life!
Connect with us & let’s start the journey
Share this article

Get in touch
Kickstart your project
with a free discovery session
Describe your idea, we explore, advise, and provide a detailed plan.